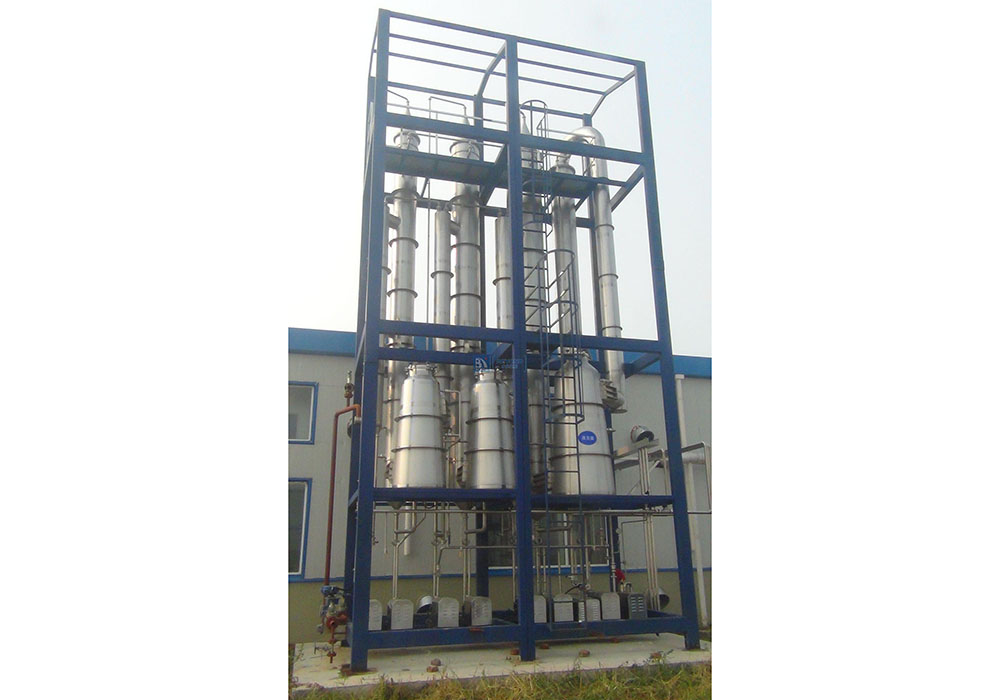
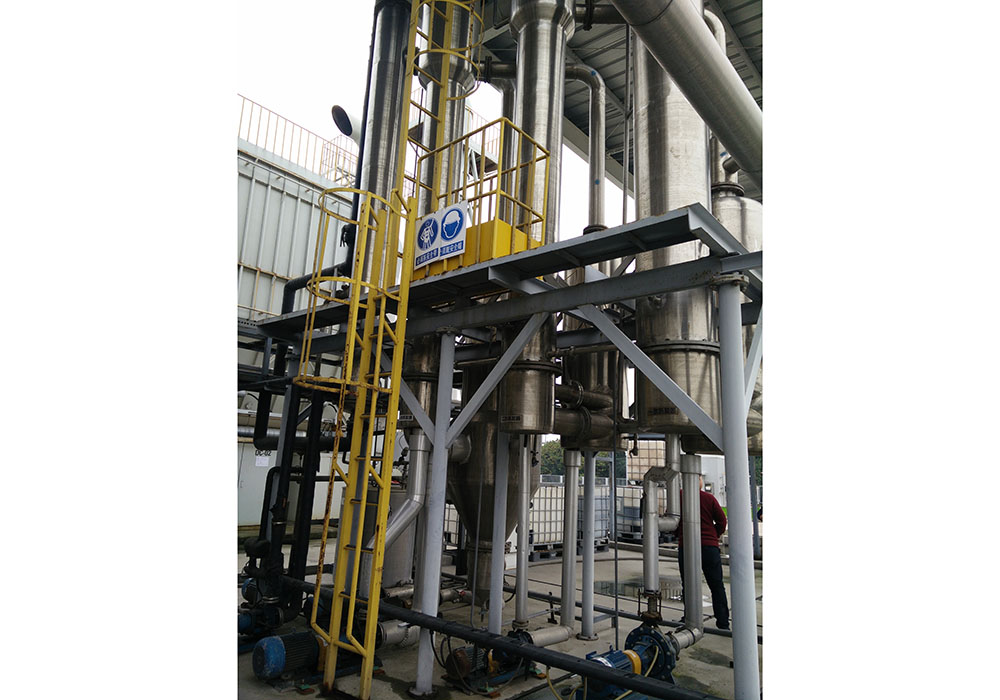
Waste Heat Evaporation System
Introduction
A waste heat evaporator uses low-grade water vapor that normally would be wasted as the heat source for the evaporator system. In the starch industry there are dryers for fiber, gluten, and germ, In the ethanol industry there are dryers for DDGS, In the dryer exhaust gas, the ratio of water vapor to air is high enough that a meaningful amount of water vapor can be used as a replacement for steam in the evaporator. Also, during the saccharification process when starch is converted into glucose, low-pressure water vapor is generated. This water vapor can also be the heat source in a multiple effect evaporator operating under vacuum.
The evaporator can be designed to use multiple sources of waste heat in one system. The waste heat can be supplemented with steam to increase the capacity. The dryer exhaust gas that passes through the evaporator and is vented to atmosphere will have considerably less dust and VOC than the original dryer gas. A scrubber can be integrated with the system to reduce SO2 emissions.
Parameter
Evaporator performance
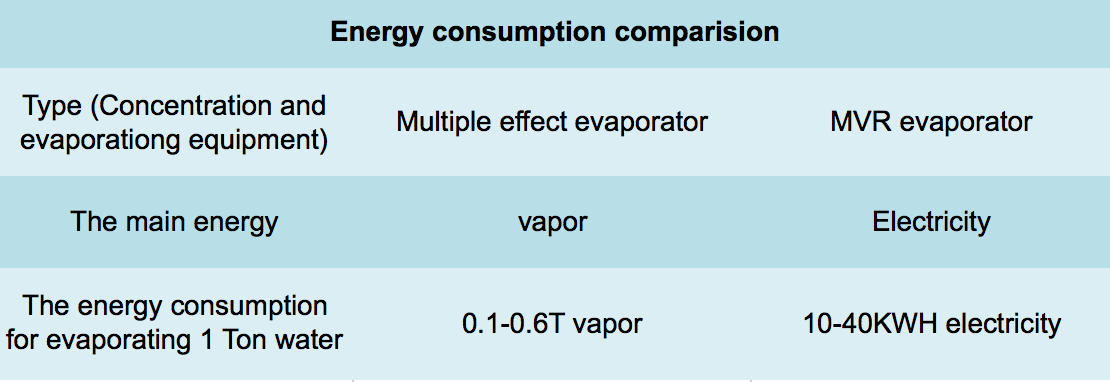
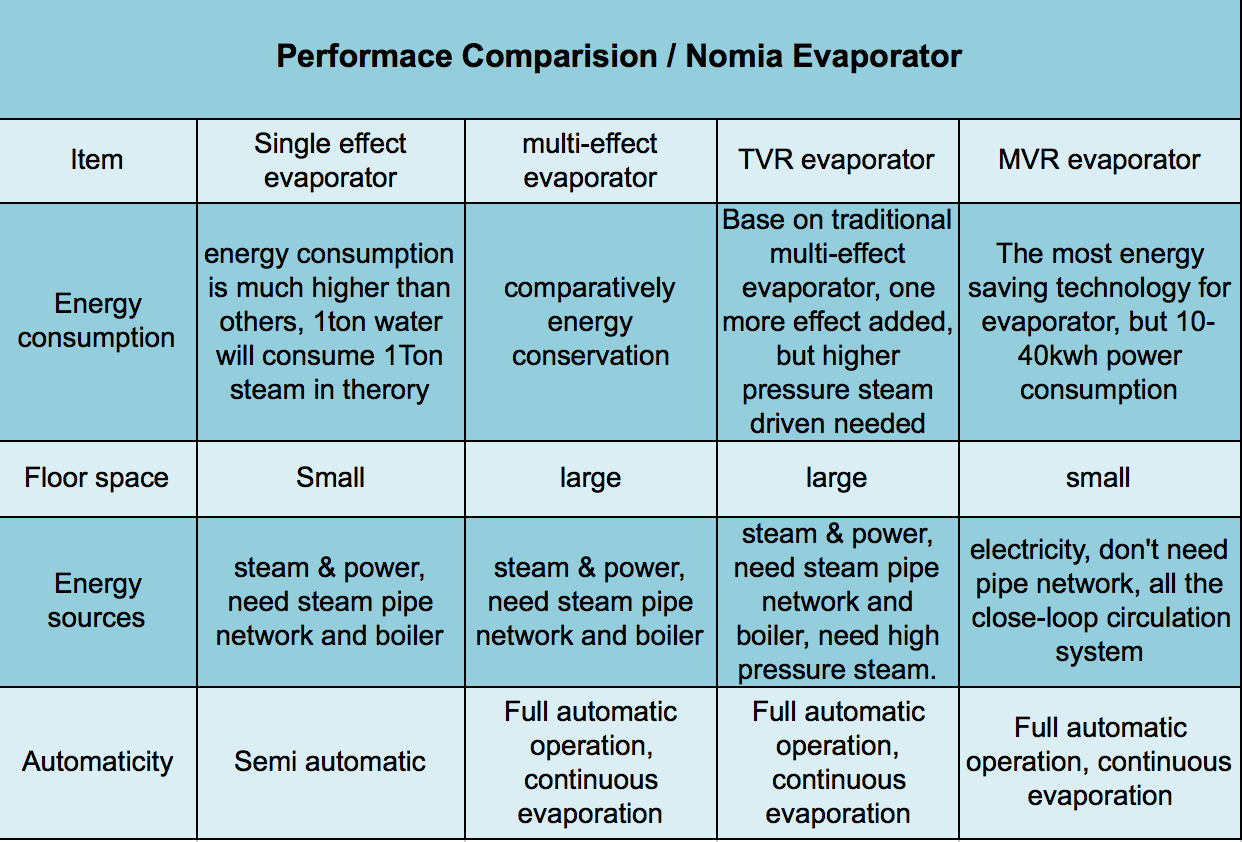 Energy consumption
Energy consumption
A waste heat evaporator uses low-grade water vapor that normally would be wasted as the heat source for the evaporator system. In the starch industry there are dryers for fiber, gluten, and germ, In the ethanol industry there are dryers for DDGS, In the dryer exhaust gas, the ratio of water vapor to air is high enough that a meaningful amount of water vapor can be used as a replacement for steam in the evaporator. Also, during the saccharification process when starch is converted into glucose, low-pressure water vapor is generated. This water vapor can also be the heat source in a multiple effect evaporator operating under vacuum.
The evaporator can be designed to use multiple sources of waste heat in one system. The waste heat can be supplemented with steam to increase the capacity. The dryer exhaust gas that passes through the evaporator and is vented to atmosphere will have considerably less dust and VOC than the original dryer gas. A scrubber can be integrated with the system to reduce SO2 emissions.
| Evaporation | 200kg/h | 500kg/h | 1000kg/h | 2000kg/h | 3000kg/h | 4000kg/h | 5000kg/h | 10000kg/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L*W*Hmm | 2000*1200*2200 | 2500*1500*2500 | 3000*1800*5200 | 3300*2400*7800 | 3500*2600*7800 | 4500*2800*10000 | 4500*3000*10000 | 6500*3800*10000 |
| area | Heater | weight/kg | Separator | weight/kg | Preheater | weight/kg | Crystallization tank | weight/kg |
| 5m² | Φ273*2400 | 170 | Φ400*700 | 40 | Φ | Φ500*1800 | 120 | |
| 10 | Φ450*1725 | 330 | Φ600*1800 | 120 | Φ | Φ700*2000 | 180 | |
| 15 | Φ550*1775 | 460 | Φ700*1800 | 170 | Φ | Φ800*2200 | 230 | |
| 20 | Φ550*2275 | 560 | Φ800*1900 | 220 | Φ | Φ900*2300 | 290 | |
| 30 | Φ650*2326 | 800 | Φ900*2000 | 280 | Φ | Φ900*2600 | 340 | |
| 40 | Φ750*2276 | 1040 | Φ900*2450 | 320 | Φ | Φ1000*3000 | 400 | |
| 50 | Φ700*3750 | 1240 | Φ1000*2450 | 390 | Φ | Φ1100*3000 | 450 | |
| 60 | Φ750*3776 | 1430 | Φ1100*2450 | 480 | Φ | Φ1200*3200 | 510 | |
| 70 | Φ800*4200 | 1450 | Φ1100*2750 | 540 | Φ | Φ1300*3200 | 580 | |
| 80 | Φ750*5176 | 1750 | Φ1200*3000 | 600 | Φ | Φ1300*3300 | 650 | |
| 90 | Φ550*7075 | 2000 | Φ1200*3300 | 650 | Φ | Φ1400*3500 | 730 | |
| 100 | Φ700*7200 | 2300 | Φ1200*3600 | 720 | Φ | Φ1500*3700 | 800 | |
| 110 | Φ750*7176 | 2540 | Φ1300*3650 | 800 | Φ | Φ1500*3800 | 850 | |
| 120 | Φ780*7176 | 2750 | Φ1300*3850 | 870 | Φ | Φ1600*3800 | 910 | |
| 130 | Φ800*7200 | 2990 | Φ1400*3900 | 940 | Φ | Φ1600*3900 | 960 | |
| 140 | Φ820*7226 | 3220 | Φ1400*4100 | 1000 | Φ | Φ1700*3900 | 1010 | |
| 150 | Φ850*7226 | 3450 | Φ1500*4150 | 1075 | Φ | Φ1700*4000 | 1060 | |
| 160 | Φ880*7226 | 3680 | Φ1500*4350 | 1150 | Φ | Φ1700*4100 | 1100 | |
| 170 | Φ880*7226 | 3850 | Φ1600*4200 | 1230 | Φ | Φ1800*4100 | 1150 | |
| 180 | Φ900*7250 | 4140 | Φ1600*4400 | 1280 | Φ | Φ1800*4200 | 1200 | |
| 190 | Φ920*7250 | 4350 | Φ1700*4600 | 1360 | Φ | Φ1800*4300 | 1240 | |
| 200 | Φ950*7300 | 4540 | Φ1800*4900 | 1440 | Φ | Φ1800*4500 | 1280 |


TOP